Cloud Computing Security: Protecting Your Data in The Cloud

Cloud computing security refers to the protection of data, applications, and infrastructure in cloud environments against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security risks. As organizations increasingly adopt cloud services, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data becomes paramount. The following sections will delve deeper into the specific risks associated with cloud computing and provide recommendations for mitigating them.
Understanding Cloud Security Risks
Data Breaches
Data breaches can have severe consequences for businesses, leading to reputational damage, financial loss, and legal liabilities. Cloud environments can be targeted by cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. Implementing robust security measures such as encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems is essential to prevent data breaches.
Unauthorized Access
Unauthorized access is another significant cloud computing security risk in the cloud. Weak passwords, compromised user accounts, and misconfigured access controls can allow malicious individuals to gain unauthorized entry to cloud resources. To mitigate this risk, organizations should enforce strong authentication mechanisms, implement multi-factor authentication, and regularly review and update access privileges.
Insecure APIs
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) act as bridges between different software components, enabling seamless communication. However, insecure APIs can provide an entry point for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities and compromise cloud systems. It is crucial to secure APIs through proper authentication, access controls, and input validation to prevent unauthorized access and data manipulation.
Data Loss
Data loss can occur due to various factors, including hardware failures, natural disasters, or human errors. Cloud providers typically implement robust data backup and disaster recovery mechanisms to ensure data availability and integrity. It is essential for organizations to regularly back up their data and test the restoration process to minimize the impact of data loss incidents.

Compliance and Legal Issues
When storing and processing data in the cloud, organizations must comply with applicable regulations and industry standards to avoid legal consequences and reputational damage. Failure to adhere to regulations such as the GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and others can result in substantial fines and loss of customer trust. Organizations should thoroughly understand the compliance requirements and work with cloud providers that offer compliant services.
Best Practices for Cloud computing security
Implementing best practices for cloud security is vital to safeguard your data. Here are some key recommendations:
Strong Authentication and Access Controls
Enforce strong password policies, implement multi-factor authentication, and regularly review and update access privileges to prevent unauthorized access.
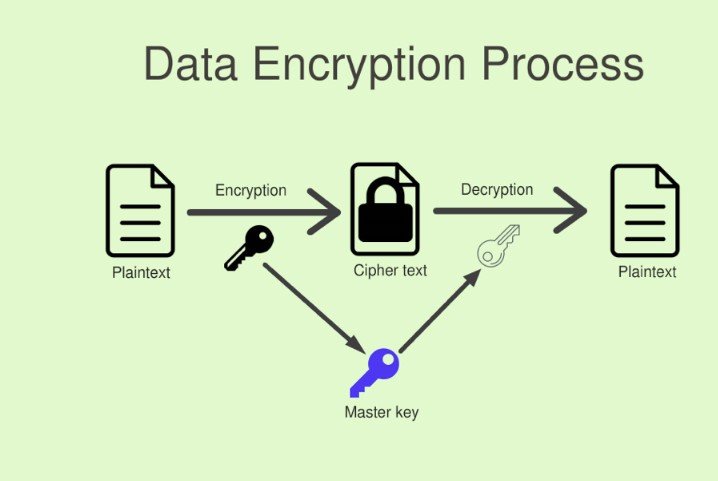
Data Encryption
Implement encryption mechanisms to protect sensitive data at rest and in transit. Encryption ensures that even if the data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the encryption keys.
Regular Data Backups
Regularly back up your data and test the restoration process to ensure data availability in case of data loss incidents.
Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Implement robust security monitoring systems to detect and respond to potential threats promptly. Have an incident response plan in place to mitigate the impact of security incidents.
Employee Training and Awareness
Educate employees about cloud security best practices, including safe data handling, password hygiene, and how to identify and report security incidents.
Selecting a Cloud computing security Provider
Choosing a secure cloud provider is crucial for ensuring the security of your data in the cloud. Consider the following factors when evaluating cloud providers:
Assessing Provider Security Measures
Review the security measures implemented by cloud providers, including physical security, network security, data encryption, and access controls.
Evaluating Data Privacy Policies
Understand the cloud provider’s data privacy policies, including data handling, data residency, and data ownership. Ensure that the provider aligns with your organization’s privacy requirements.
Compliance with Industry Standards
Verify if the cloud provider adheres to industry standards and regulations relevant to your business. This includes certifications such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, and compliance with GDPR or HIPAA requirements.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Assess the cloud provider’s disaster recovery and business continuity capabilities to ensure your data remains available and recoverable in case of disruptions.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Review the SLAs provided by the cloud provider to understand the level of service, uptime guarantees, and response times during incidents.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Compliance with regulations and industry standards is essential when utilizing cloud services. Here are some key considerations:
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
The GDPR imposes strict requirements on the handling of personal data. Ensure that your cloud provider complies with GDPR regulations and provides adequate data protection mechanisms.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
If your organization deals with protected health information (PHI), ensure that your cloud provider offers HIPAA-compliant services and safeguards PHI accordingly.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
For businesses that process credit card transactions, choose a cloud provider that complies with PCI DSS requirements to protect cardholder data.
SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2)
SOC 2 compliance ensures that cloud providers have proper controls in place to protect customer data and meet specific trust services criteria.
ISO 27001 (Information Security Management System)
ISO 27001 certification demonstrates that a cloud provider follows best practices for information security management systems.
Hybrid Cloud computing security
Hybrid cloud environments, combining public and private cloud services, offer enhanced flexibility and scalability. However, securing hybrid cloud architectures comes with its own challenges:
Benefits and Challenges Cloud computing security
Explore the benefits and challenges of adopting a hybrid cloud model, including data integration, security coordination, and complexity management.
Implementing Secure Hybrid Cloud Environments
Establish secure connectivity between public and private clouds, ensure consistent security policies, and implement proper access controls across the hybrid environment.
Integration and Data Transfer Security
Secure data transfers between public and private clouds, considering encryption, secure protocols, and secure gateways.
Identity and Access Management
Implement a unified identity and access management system to ensure consistent access controls and identity federation across the hybrid cloud environment.
Network Security
Protect the network connections and traffic flow between public and private cloud resources through network segmentation, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
Emerging Technologies in Cloud Computing Security
Several emerging technologies are revolutionizing cloud security practices. Here are a few notable ones:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Threat Detection
AI-powered threat detection systems can analyze large amounts of data, identify patterns, and detect anomalies or potential security breaches in real-time.
Blockchain for Data Integrity
Blockchain technology offers tamper-proof and transparent data storage, ensuring data integrity and providing an auditable trail of transactions.
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs)
CASBs act as intermediaries between cloud service users and providers, providing additional security controls, data loss prevention, and threat intelligence.
Secure DevOps
Secure DevOps practices integrate security into the development and deployment processes, enabling faster and more secure delivery of cloud-based applications.
Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture emphasizes strict access controls, authentication, and continuous monitoring to ensure that every access attempt is verified, regardless of location or user.
Conclusion
Protecting your data in the cloud is of utmost importance in today’s digital landscape. By understanding the risks, implementing best practices, and selecting secure cloud providers, you can mitigate potential security threats and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your valuable data.
ReadMore: 10 Best Advantages of Cloud Computing for Business 2023
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How can I ensure the security of my data in the cloud?
To ensure the security of your data in the cloud, follow these best practices:
- Implement strong authentication and access controls
- Encrypt your data at rest and in transit
- Regularly back up your data
- Monitor your cloud environment for potential threats
- Train your employees on cloud security best practices
What are the common security risks associated with cloud computing?
Common security risks in cloud computing include data breaches, unauthorized access, insecure APIs, data loss, and compliance and legal issues.
How do I choose a secure cloud provider?
When selecting a cloud provider, assess their security measures, evaluate their data privacy policies, ensure compliance with industry standards, and review their disaster recovery and business continuity capabilities.
What compliance and regulatory considerations should I be aware of?
Key compliance and regulatory considerations include GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOC 2, and ISO 27001. Ensure that your cloud provider meets the specific requirements relevant to your industry.
Are there any emerging technologies that can enhance cloud security?
Yes, emerging technologies such as AI for threat detection, blockchain for data integrity, CASBs, Secure DevOps, and Zero Trust Architecture are enhancing cloud security practices and providing additional layers of protection.
ReadMore: Exploring Thin Client Solutions: Streamlining Computing Infrastructure











